Difference between revisions of "Usability and UX Questionnaires"
(→Software Usability Measurement Inventory (SUMI)) |
(→System Usability Scale (SUS)) |
||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
== System Usability Scale (SUS) == | == System Usability Scale (SUS) == | ||
| − | * Source / Weblink / Publication | + | == System Usability Scale (SUS) == |
| − | * Administration, Procedure (paper, online, time needed, post-hoc) | + | |
| − | * Structure (e.g. number of items, constructs) | + | * Source / Weblink / Publication |
| + | - Brooke, J., 1996. SUS: A ‘quick and dirty’ usability scale. In: Jordan, P., Thomas, B., Weerdmeester, B. (Eds.), | ||
| + | Usability Evaluation in Industry. Taylor & Francis, London, UK, pp. 189–194. | ||
| + | * Administration, Procedure (paper, online, time needed, post-hoc) | ||
| + | - User fills in the SUS directly after using the app/platform prior to possible discussions | ||
| + | - can be done online and paper | ||
| + | - free to use, just needs to be mentioned | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Structure (e.g. number of items, constructs) | ||
| + | - 10 items, the odd-numbered items have a positive tone; the even-numbered items a negative tone | ||
| + | - rating from 1 to 5 (disagree - strongly agrees) | ||
| + | - SUS scores range from 0 to 100 in 2.5 point increments | ||
| + | - calculation instructions (excel sheet): http://www.measuringux.com/SUS_Calculation.xls | ||
| + | |||
* Quality (e.g. Reliability, Validity, Intrusiveness etc.) | * Quality (e.g. Reliability, Validity, Intrusiveness etc.) | ||
| + | - reliability > 0.90 | ||
| + | - sensitive to different types of devices or systems | ||
| + | - significant relationship between SUS scores and a composite metric based on business indicators of success in the marketplace | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Potential Disadvantages | ||
| + | - misinterpretation | ||
| + | - mistake: users do not agree or disagree in the sense they want to because of changing tone | ||
| + | - miscode: researchers do calculation error | ||
== User Experience Questionnaire (UEQ) == | == User Experience Questionnaire (UEQ) == | ||
Revision as of 06:09, 9 June 2020
Please describe the different Usability and UX Questionnaires in terms of
- Name of the questionnaire
- Source / Weblink / Publication
- Administration, Procedure (paper, online, time needed, post-hoc)
- Structure (e.g. number of items, constructs)
- Quality (e.g. Reliability, Validity, Intrusiveness etc.)
Contents
AttrakDiff
IsoNorm
Isometrics
Group 4 is checking this.
Source / Weblink / Publication:
file:///Users/valeriafugazza/Downloads/ISOMetrics_S.pdf
Gediga, Günther & Hamborg, Kai-Christoph & Duntsch,. (1999). The IsoMetrics Usability Inventory. An operationalisation of ISO 9241-10 supporting summative and formative evaluation of software systems. Behaviour and Information Technology. 18. 151-164. 10.1080/014492999119057.
Administration, Procedure (paper, online, time needed, post-hoc):
The Isometrics test is performed online
-The mean time to perform this test is 1.5 hours (long version)
-The mean time to perform this test is 30 minutes (short version)
Structure (e.g. number of items, constructs):
-The number of items is 75 with an additional weighting and open answers with examples (long version)
-The questionnaire consisted of 75 items based on the seven principles of suitability for the task, self-descriptiveness, controllability, conformity with user expectations, error tolerance, suitability for individualization, and suitability for learning.
-The number of items is 35 by just using Likert-like questions (short version)
-IsoMetrics contains a five point rating for each of the items starting from one (`predominantly disagree’) to (`predominantly agree’) including (`no opinion’)
-Seven scores of the usability dimension to measure the progress of development
-Concrete information about malfunctions and their user-perceived attributes
-Mean weight of any user-perceived attribute given a class of system malfunctions.
Quality (e.g. Reliability, Validity, Intrusiveness etc.):
-It is deemed a valuable and reliable tool
-Inter-rater reliability turns out to be very high (Cohen’s kap- pa = 0.95)
-High reliability of sub-scales
System Usability Scale (SUS)
System Usability Scale (SUS)
- Source / Weblink / Publication
- Brooke, J., 1996. SUS: A ‘quick and dirty’ usability scale. In: Jordan, P., Thomas, B., Weerdmeester, B. (Eds.), Usability Evaluation in Industry. Taylor & Francis, London, UK, pp. 189–194.
- Administration, Procedure (paper, online, time needed, post-hoc)
- User fills in the SUS directly after using the app/platform prior to possible discussions - can be done online and paper - free to use, just needs to be mentioned
- Structure (e.g. number of items, constructs)
- 10 items, the odd-numbered items have a positive tone; the even-numbered items a negative tone - rating from 1 to 5 (disagree - strongly agrees) - SUS scores range from 0 to 100 in 2.5 point increments - calculation instructions (excel sheet): http://www.measuringux.com/SUS_Calculation.xls
- Quality (e.g. Reliability, Validity, Intrusiveness etc.)
- reliability > 0.90 - sensitive to different types of devices or systems - significant relationship between SUS scores and a composite metric based on business indicators of success in the marketplace
- Potential Disadvantages
- misinterpretation - mistake: users do not agree or disagree in the sense they want to because of changing tone - miscode: researchers do calculation error
User Experience Questionnaire (UEQ)
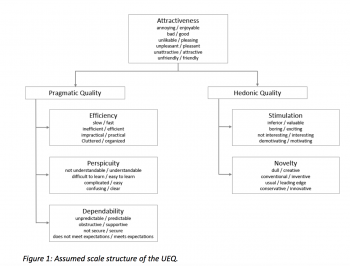
The scales of the questionnaire cover a comprehensive impression of user experience. Both classical usability aspects (efficiency, perspicuity, dependability) and user experience aspects (originality, stimulation) are measured.
Source / Weblink / Publication
- You can download the questionnaire for free on this website: https://www.ueq-online.org/
- published by the UEQ Team
Administration, Procedure (paper, online, time needed, post-hoc)
- questionnaire to evaluate a product based on contrasting attributes on a 7-point-scale
- accessible as a PDF download or as an online questionnaire
- either filled out online or on paper
- Full version and short version available
- Time needed for full version approx. 5-10 minutes
Structure (e.g. number of items, constructs)
The UEQ Full Version contains 6 scales with 26 items (https://www.ueq-online.org/Material/Handbook.pdf):
- Attractiveness: Overall impression of the product. Do users like or dislike the product?
- Perspicuity: Is it easy to get familiar with the product? Is it easy to learn how to use the product?
- Efficiency: Can users solve their tasks without unnecessary effort?
- Dependability: Does the user feel in control of the interaction?
- Stimulation: Is it exciting and motivating to use the product?
- Novelty: Is the product innovative and creative? Does the product catch the interest of users?
Short version: 8 items 3-5 Minutes
Quality (e.g. Reliability, Validity, Intrusiveness etc.)
- gives idea about the perception of different characteristics of a product
- good construct validity, measured with Cronbach's Alpha
- not intrusive
Software Usability Measurement Inventory (SUMI)
Source: / Weblink / Publication: http://sumi.uxp.ie/en/
Description: ISO/IEC 9126 tries to develop a common understanding of the project's objectives and goals. SUMI is supported by an extensive reference database and an analysis and report generation tool called SUMISCO. The standard is divided into four parts: quality model external metrics internal metrics quality in use metrics
Administration and Procedure:
Online SUMI requires sample sizes with a minimum of about 20 unless your respondents are well selected. Once the questionnaire is filled, submit results to online and a report would be sent. Time : 15 - 20 mins
Structure :
SUMI consists of 50 statements to which the user has to reply that they either Agree, Don't Know, or Disagree. 20 languages The Overall Assessment down into 5 sub-scales: 1.Affect: how much the product captures the user's emotional responses. 2.Efficiency: degree to which the user can achieve the goals of his interaction with the product in a direct and timely manner. 3.Helpfulness; extent to which the product seems to assist the user 4.Control: degree to which the user feels he, and not the product, is setting the pace. 5.Learnability: ease with which a user can get started and learn new features of the product
Quality:
Validity & Reliability: SUMI enables measurement of some of the user-orientated requirements expressed in the European Directive on Minimum Health and Safety Requirements for Work with Display Screen Equipment(90/270/EEC).. Three different kinds of validity studies have been conducted with SUMI: I)the industrial partners within the MUSiC consortium used SUMI as part of the industry-scale validation of the MUSiC usability evaluation toolset. II)there are now a number of laboratory-based studies which have been carried out in the Human Factors Research Group. III)studies which have been carried out for industrial clients on a consultancy basis. consultancy studies are nearly always commissioned on the understanding of strict confidentiality agreements and are not disclosable in public except in vague outline
Example of the report :
Usability Metric For User Experience (UMUX)
Group 2 is doing this :)