Usability and UX Questionnaires
Please describe the different Usability and UX Questionnaires in terms of
- Name of the questionnaire
- Source / Weblink / Publication
- Administration, Procedure (paper, online, time needed, post-hoc)
- Structure (e.g. number of items, constructs)
- Quality (e.g. Reliability, Validity, Intrusiveness etc.)
Contents
- 1 AttrakDiff
- 2 Post-Study Usability Questionnaire (PSSUQ)
- 3 Standardized User Experience Percentile Rank Questionnaire (SUPR-Q)
- 4 mHealth App Usability Questionnaire (MAUQ)
- 5 IsoNorm 9241/10
- 6 Isometrics
- 7 System Usability Scale (SUS)
- 8 User Experience Questionnaire (UEQ)
- 9 Software Usability Measurement Inventory (SUMI)
- 10 Usability Metric For User Experience (UMUX)
- 11 Usability Magnitude Estimation (UME)
- 12 Website Analysis and Measurement Inventory (WAMMI)
AttrakDiff
Duru & Anton
- Source / Weblink / Publication
- for general introduction
- to test the questionnaire
- Administration, Procedure (paper, online, time needed, post-hoc)
- The test is performed online. There is no defined time to complete the questionnaire.
Goal: To give you an understanding of how users rate the usability and design of your interactive product. It provides you a broad overview of your project.
- Structure (e.g. number of items, constructs)
- This questionnaire is made up of 28 items originally, distributed in 4 dimensions, each comprising 7 items. These 28 items in total are scored from -3 to 3.
Dimensions:
1. Pragmatic usability, which measures the usability of the product
2. Hedonic-stimulation usability which measures the stimulation generated by the system.
3. Hedonic-identification usability, which measures the identification of the user with the system.
4. Overall attractiveness, which measures the overall attractiveness of the system, based on pragmatic and hedonic qualities.
- Although known for its original version of 28 items, there is also a shorter version of 10 items, to reduce the completion time.
- Quality (e.g. Reliability, Validity, Intrusiveness etc.)
-
- The AttrakDiff is an empirically validated user experience questionnaire that measures both pragmatic and hedonic quality (Hassenzahl et al., 2003).
Reliability Cronbachs α Scores of the subscales are: HQ-S α = ,76 - ,90 HQ-I α = ,73 - ,83 PQ α= ,83 - ,85
The reference article: https://dl.gi.de/server/api/core/bitstreams/5a6da40f-5018-49e2-b0fd-58e9f49dad71/content
- Pros
- You can isolate one of the four subscales, if you want to.
The test is free of charge.
Two language options: German and English.
Graphs are provided with the analysis, which makes it easier to comprehend.
- Cons
- It is recommended to not to use it for wireframe prototypes. *
Post-Study Usability Questionnaire (PSSUQ)
Theresa & Moritz
- Source / Weblink / Publication
- Administration, Procedure (paper, online, time needed, post-hoc)
-
- Structure (e.g. number of items, constructs)
-
- Quality (e.g. Reliability, Validity, Intrusiveness etc.)
-
- Pros
-
- Cons
-
Standardized User Experience Percentile Rank Questionnaire (SUPR-Q)
Liubou & Helena
- Source / Weblink / Publication
- https://measuringu.com/product/suprq/
- Administration, Procedure (paper, online, time needed, post-hoc)
-
- Structure (e.g. number of items, constructs)
-
- Quality (e.g. Reliability, Validity, Intrusiveness etc.)
-
- Pros
-
- Cons
-
mHealth App Usability Questionnaire (MAUQ)
- Source / Weblink / Publication
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30973342/ (Description and Abstract only)
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6482399/ (Full text)
- Administration, Procedure (paper, online, time needed, post-hoc)
-
- Structure (e.g. number of items, constructs)
-
- Quality (e.g. Reliability, Validity, Intrusiveness etc.)
-
- Pros
-
- Cons
-
IsoNorm 9241/10
- Source / Weblink / Publication
- Paper from Jochen Prümper, the author of the questionnaire (in German)
- Downlaod German Version
- Paper from Kathrin Figl on IsoNorm and Isometrics, comparing the two (in German)
- Administration, Procedure (paper, online, time needed, post-hoc)
-
- Structure (e.g. number of items, constructs)
-
- Quality (e.g. Reliability, Validity, Intrusiveness etc.)
-
- Pros
-
- Cons
-
Isometrics
- Source / Weblink / Publication
- Gediga, Günther & Hamborg, Kai-Christoph & Duntsch,. (1999). The IsoMetrics Usability Inventory. An operationalisation of ISO 9241-10 supporting summative and formative evaluation of software systems. Behaviour and Information Technology. 18. 151-164. https://doi.org/10.1080/014492999119057
- Administration, Procedure (paper, online, time needed, post-hoc)
- The Isometrics test is performed online
- The mean time to perform this test is 1.5 hours (long version)
- The mean time to perform this test is 30 minutes (short version)
- Structure (e.g. number of items, constructs)
-
- The number of items is 75 with an additional weighting and open answers with examples (long version)
- The questionnaire consisted of 75 items based on the seven principles of suitability for the task, self-descriptiveness, controllability, conformity with user expectations, error tolerance, suitability for individualization, and suitability for learning.
- The number of items is 35 by just using Likert-like questions (short version)
- IsoMetrics contains a five point rating for each of the items starting from one (`predominantly disagree’) to (`predominantly agree’) including (`no opinion’)
- Seven scores of the usability dimension to measure the progress of development
- Concrete information about malfunctions and their user-perceived attributes
- Mean weight of any user-perceived attribute given a class of system malfunctions.
- Quality (e.g. Reliability, Validity, Intrusiveness etc.)
-
- It is deemed a valuable and reliable tool
- Inter-rater reliability turns out to be very high (Cohen’s kap- pa = 0.95)
- High reliability of sub-scales
System Usability Scale (SUS)
- Source / Weblink / Publication
- Brooke, J., 1996. SUS: A ‘quick and dirty’ usability scale. In: Jordan, P., Thomas, B., Weerdmeester, B. (Eds.), Usability Evaluation in Industry. Taylor & Francis, London, UK, pp. 189–194.
- Administration, Procedure (paper, online, time needed, post-hoc)
-
- User fills in the SUS directly after using the app/platform prior to possible discussions
- can be done online and paper
- free to use, just needs to be mentioned
- Structure (e.g. number of items, constructs)
-
- 10 items, the odd-numbered items have a positive tone; the even-numbered items a negative tone
- rating from 1 to 5 (disagree - strongly agrees)
- SUS scores range from 0 to 100 in 2.5 point increments
- calculation instructions (excel sheet): http://www.measuringux.com/SUS_Calculation.xls
- Quality (e.g. Reliability, Validity, Intrusiveness etc.)
-
- reliability > 0.90
- sensitive to different types of devices or systems
- significant relationship between SUS scores and a composite metric based on business indicators of success in the marketplace
- Potential Disadvantages
-
- misinterpretation
- mistake: users do not agree or disagree in the sense they want to because of changing tone
- miscode: researchers do calculation error
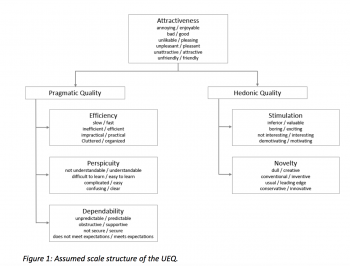
User Experience Questionnaire (UEQ)
The scales of the questionnaire cover a comprehensive impression of user experience. Both classical usability aspects (efficiency, perspicuity, dependability) and user experience aspects (originality, stimulation) are measured.
Source / Weblink / Publication
- You can download the questionnaire for free on this website: https://www.ueq-online.org/
- published by the UEQ Team
Administration, Procedure (paper, online, time needed, post-hoc)
- questionnaire to evaluate a product based on contrasting attributes on a 7-point-scale
- accessible as a PDF download or as an online questionnaire
- either filled out online or on paper
- Full version and short version available
- Time needed for full version approx. 5-10 minutes
Structure (e.g. number of items, constructs)
The UEQ Full Version contains 6 scales with 26 items (https://www.ueq-online.org/Material/Handbook.pdf):
- Attractiveness: Overall impression of the product. Do users like or dislike the product?
- Perspicuity: Is it easy to get familiar with the product? Is it easy to learn how to use the product?
- Efficiency: Can users solve their tasks without unnecessary effort?
- Dependability: Does the user feel in control of the interaction?
- Stimulation: Is it exciting and motivating to use the product?
- Novelty: Is the product innovative and creative? Does the product catch the interest of users?
Short version: 8 items 3-5 Minutes
Quality (e.g. Reliability, Validity, Intrusiveness etc.)
- gives idea about the perception of different characteristics of a product
- good construct validity, measured with Cronbach's Alpha
- not intrusive
Software Usability Measurement Inventory (SUMI)
Source: / Weblink / Publication: http://sumi.uxp.ie/en/
Description: ISO/IEC 9126 tries to develop a common understanding of the project's objectives and goals. SUMI is supported by an extensive reference database and an analysis and report generation tool called SUMISCO. The standard is divided into four parts: quality model external metrics internal metrics quality in use metrics
Administration and Procedure:
Online SUMI requires sample sizes with a minimum of about 20 unless your respondents are well selected. Once the questionnaire is filled, submit results to online and a report would be sent. Time : 15 - 20 mins
Structure :
SUMI consists of 50 statements to which the user has to reply that they either Agree, Don't Know, or Disagree. 20 languages The Overall Assessment down into 5 sub-scales: 1.Affect: how much the product captures the user's emotional responses. 2.Efficiency: degree to which the user can achieve the goals of his interaction with the product in a direct and timely manner. 3.Helpfulness; extent to which the product seems to assist the user 4.Control: degree to which the user feels he, and not the product, is setting the pace. 5.Learnability: ease with which a user can get started and learn new features of the product
Quality:
Validity & Reliability: SUMI enables measurement of some of the user-orientated requirements expressed in the European Directive on Minimum Health and Safety Requirements for Work with Display Screen Equipment(90/270/EEC).. Three different kinds of validity studies have been conducted with SUMI: I)the industrial partners within the MUSiC consortium used SUMI as part of the industry-scale validation of the MUSiC usability evaluation toolset. II)there are now a number of laboratory-based studies which have been carried out in the Human Factors Research Group. III)studies which have been carried out for industrial clients on a consultancy basis. consultancy studies are nearly always commissioned on the understanding of strict confidentiality agreements and are not disclosable in public except in vague outline
Example of the report :
Usability Metric For User Experience (UMUX)
Group 2 is doing this :) The UMUX questionnaire was intended to offer a shorter alternative to the 10-item SUS questionnaire. Whereas SUS assesses perceived usability and learnability, UMUX targets usability by assessing effectiveness, efficiency, and satisfaction.
- Source / Weblink / Publication
- There is not really a direct source that creates this for you, but there are plenty of templates that help you run it.
- Here is a good overview of the whole process: https://help.qualaroo.com/hc/en-us/articles/360039072752-UMUX-Usability-Metric-for-User-Experience-
- Administration, Procedure
- Conducting on paper or online
- Structure (e.g. number of items, constructs)
- UMUX is a simple four-item questionnaire listing two positive and two negative statements that respondents rate agreement with on a five or seven-point Likert scale. UMUX-Lite is the shorter version which only contains the positive statements.
- The four items are:
- [This system’s] capabilities meet my requirements.
- Using [this system] is a frustrating experience.
- [This system] is easy to use.
- I have to spend too much time correcting things with [this system].

- Scoring
-
- Odd items are scored as [user score - 1]. Even items are scored as [7 - user score].
- Add up these differences and divide the sum by 24 (the highest possible score).
- Multiply your quotient by 100. Average your results across users.
- If you’re using a 5-point Likert scale, you will only have to make a few adjustments to the steps above. Even items should be scored as [5 - user score] and you’ll have to divide the sum by 16 instead of 24.
- Quality (e.g. Reliability, Validity, Intrusiveness etc.)
- Reliability: Sauro and Lewis (2016) estimated UMUX reliability to be 0.87 and 0.81, and the correlations with the SUS were 0.90 (standard) and 0.79 (positive).
- Although scoring might be slightly more complicated with this specific template, the results will ensure that measuring of usability according to its standardized definition and with very little time spent on set-up!
- Because the UMUX Questionnaire is evaluated on a Likert scale, we recommend keeping potential respondent biases in mind that are associated with Likert scale reporting.
- Social desirability bias - Most people tend to give answers that they consider as socially acceptable rather than being fully honest.
- If your results are overwhelmingly positive, dig in further by reaching out to some of your respondents for in-depth user research interviews.
- Central tendency bias - Most people avoid choosing extreme responses such as 1 “Strongly disagree” or 7 “Strongly agree”
- While the UMUX questionnaire was tested and retested to help mitigate this bias, if you are finding that the majority of your responses are neutral, you might consider how the central tendency bias is at work here.
- Social desirability bias - Most people tend to give answers that they consider as socially acceptable rather than being fully honest.
- Pros
-
- The UMUX Questionnaire is an ideal length. Shorter than the System Usability Scale. Longer than the Single Ease Questionnaire. UMUX gives you a greater amount of insights that your users can provide quickly!
- UMUX evaluates usability based on the official definition and standard established by the ISO.
- Cons
-
- Scoring is somewhat more complex when it comes to UMUX, especially if you’re interested in comparing your results to an SUS score.
- Because UMUX combines both positive and negative questions, some researchers have found that it creates a two-factor test. However, UMUX-Lite can be used instead, if you find your data showing the same concern.
Usability Magnitude Estimation (UME)
https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/154193120404800536
Website Analysis and Measurement Inventory (WAMMI)
- Goal
WAMMI measures user-satisfaction by asking visitors to your website to compare their expectations with what they actually experience on the website
- Source / Weblink / Publication
http://www.wammi.com/whatis.html
- Administration, Procedure
Online Survey/Questionnaire
- Structure (e.g. number of items, constructs)
- Standarised 20-statement questionnaire and a unique international database.
- You customize your survey by asking additional questions of your choice around the 20 statements.
- It is structured into five key scales: Attractiveness, Controllability, Efficiency, Helpfulness and Learnabilit
- Reliability
Reliability data rating of between 0.90 and 0.93 . WAMMI is a scientific analytics service, iteratively developed using Psychometric techniques. It has been scientifically proven and has a reliability data rating of between 0.90 and 0.93." " It's measured in terms of five key scales: Attractiveness, Controllability, Efficiency, Helpfulness and Learnability. The Global Usability Score (GUS) exhibits a high degree of reliability, technically measured using Cronbach's Alpha coefficient, with Alpha = 0.90. This coefficient usually ranges from 0.00 (poor reliability) to 1.00 (high reliability).
The five sub-scales, being smaller, have lower intrinsic Alpha coefficients, but when adjusted for size, are comparable with the Global scale:
- Scoring
5-Point Likert Scale from 1 (Strongly Agree) to 5 (Strongly Disagree)
- Report
Your site is also given an overall Global Usability Score (GUS) for how well visitors rate your site. An average score is 50 and a perfect score is 100. The WAMMI report also contains: - An individual statement analysis, giving you more information about which aspects of your website need improving. - Cross-tabulations of all additional questions (fixed choice answers) with the GUS and the five WAMMI scales. Cross tabulations of visitor responses to check-box questions with the GUS and the five WAMMI scales. - Unedited responses to free-text questions where visitors comment about things not specifically asked for by the WAMMI statements. - Individual visitor profiles and a numeric summary of the WAMMI results.
- Pros
WAMMI is currently available in the following languages: Danish, Dutch, English, Finnish, French, German, Italian, Norwegian, Polish, Portuguese (European), Spanish and Swedish.
- Cons
You need to include the entire set of sub-scales into your testing for a high reliability.